Answer:
Explanation:
The standard form of a quadratic equation is y=
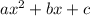 where a, b, and c are coefficients and x, y are variables.
where a, b, and c are coefficients and x, y are variables.
The vertex form of a quadratic equation is y=
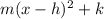 where m represents the slope of the line and h and k are any points on the line.
where m represents the slope of the line and h and k are any points on the line.
To convert a quadratic equation from the standard form to the vertex form we follow the following steps:
1. Factor coefficient: Factorise the standard form of the quadratic equation by finding the pair of numbers that add up to b and multiply to ac. For example consider the quadratic equation,
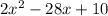 , factorise this equation as
, factorise this equation as
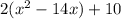 .
.
2. Divide coefficient: Divide the coefficient of the x term inside the excursion by 2.Square that number using the square root property. In this example, the coefficient of x is -14.
3. Balance equation: Add the number inside the excursion, and then in order to balance the equation, multiply it by the factor on the outside of excursion and subtract this number from the whole quadratic equation.
For example
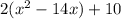 becomes
becomes
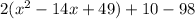 as 49×2=98. Now, simplify the equations by combining the terms that is
as 49×2=98. Now, simplify the equations by combining the terms that is
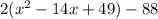 .
.
4. Convert terms: Convert the terms inside excursion to a squared unit of the form
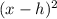 . The value of h is equal to half the coefficient of the x term. thus,
. The value of h is equal to half the coefficient of the x term. thus,
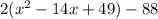 becomes
becomes
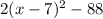 and the equation becomes in the vertex form.
and the equation becomes in the vertex form.