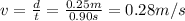1. Average time for the first 0.25 m: 2.23 s
Step-by-step explanation:
The average time that it takes for the car to travel the first 0.25 m is given by the average of the first three measures, so:
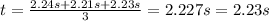
2. Average time to travel between 0.25 m and 0.50 m: 0.90 s
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we need to calculate the time the car takes to travel between 0.25 m and 0.50 m for each trial:
t1 = 3.16 s - 2.24 s = 0.92 s
t2 = 3.08 s - 2.21 s = 0.87 s
t3 = 3.15 s - 2.23 s = 0.92 s
So, the average time is
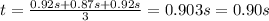
3. Velocity in the second 0.25 m section: 0.28 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The average velocity in the second 0.25 m section is equal to the ratio between the distance covered (0.25 m) and the average time taken (0.90 s):