Answer:
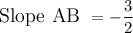
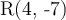
Explanation:
The formula of a slope:
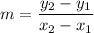
We have the points A(-6, 8) and B(-2, 2). Substitute:
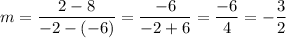
The hypotenuse of triangle QRS is on the same line as the hypotenuse of triangle ABC. Therefore the line QR has the same slope as the line AB.
We have Q(2, -4) and R(x, y). Substitute to the formula of a slope:
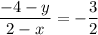 cross multiply
cross multiply
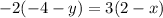 use distributive property
use distributive property
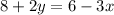 subreac 8 from both sides
subreac 8 from both sides
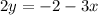 divide both sides by 2
divide both sides by 2
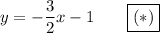
The hypotenuse of triangle QRS is one-half the length of AB.
The formula of a distance between two points:
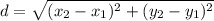
Calculate the distance between A and B:
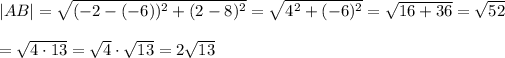
Therefore
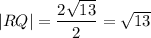
Substitute coordinates of the point R(x, y) and Q(2, -4) to the formula of a distance between two points:
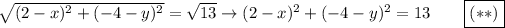
Substitute
 to
to
 :
:
![(2-x)^2+\left[-4-\left(-(3)/(2)x-1\right)\right]^2=13\\\\(2-x)^2+\left(-4+(3)/(2)x+1\right)^2=13\\\\(2-x)^2+\left((3)/(2)x-3\right)^2=13\qquad\text{use}\ (a-b)^2=a^2-2ab+b^2\\\\2^2-2(2)(x)+x^2+\left((3)/(2)x\right)^2-2\left((3)/(2)x\right)(3)+3^2=13\\\\4-4x+x^2+(9)/(4)x^2-9x+9=13\qquad\text{combine like terms}\\\\\left((4)/(4)x^2+(9)/(4){x^2}\right)+(-4x-9x)+(4+9)=13\\\\(13)/(4)x^2-13x+13=13\qquad\text{subtract 13 from both sides}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/txwr4hihaomu8p5j8yzghye4gsx4ws1xex.png)
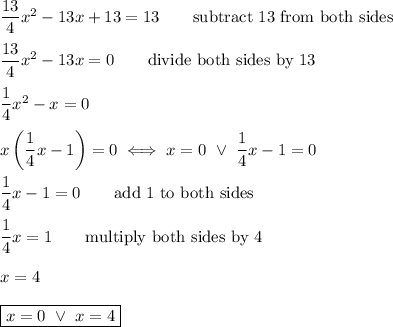
Put the values of x to

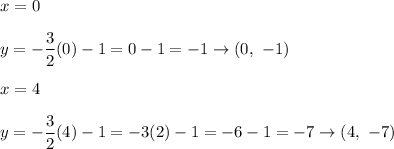
As the triangle ABC and the QRS triangle are similar, then AB corresponds to QR not RQ. Thus, the coordinates of the R point are (4, -7).
Look at the picture.