Answer:
908 g Fe₂O₃
General Formulas and Concepts:
Chemistry - Gas Laws
Combined Gas Law: PV = nRT
- P is pressure
- V is volume (in liters)
- n is number of moles
- R is a constant -
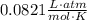
- T is temperature (in Kelvins)
Chemistry - Stoichiometry
- Reading a Periodic Table
- Using Dimensional Analysis
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Define
[RxN] 2Fe₂O₃ (s) + 3C (s) → 4Fe (s) + 3CO₂ (g)
[Given] 100 L CO₂ at 300 K and 2.10 atm
Step 2: Find Moles
Apply the Combined Gas Law and solve.
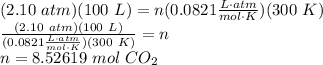
Step 3: Identify Conversions
[RxN] 3 mol CO₂ = 2 mol Fe₂O₃
Molar Mass of Fe - 55.85 g/mol
Molar Mass of O - 16.00 g/mol
Molar Mass of Fe₂O₃ - 2(55.85) + 3(16.00) = 159.7 g/mol
Step 4: Stoichiometry
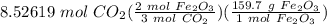 = 907.755 g Fe₂O₃
= 907.755 g Fe₂O₃
Step 5: Check
We are given 3 sig figs. Follow sig fig rules and round.
907.755 g Fe₂O₃ ≈ 908 g Fe₂O₃