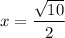Answer:
a:
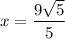 .
.
b:
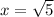 .
.
c:
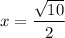 .
.
Explanation:
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem. The square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is the sum of the squares of the two legs.
For triangle in a:
- Hypotenuse: 9.
- First Leg: x.
- Second Leg: 2x.
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem.
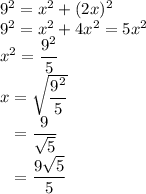
 .
.
As a result,
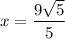 .
.
Try the same steps for the triangle in b.
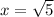 .
.
Question c includes a rectangle. The lengths of opposite sides of a rectangle are equal. As a result, for the right triangle with a right angle at the lower-right corner of the rectangle:
- Hypotenuse: 5.
- First Leg: x.
- Second Leg: 2x.
Apply the Pythagorean Theorem:
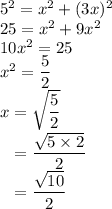
As a result,