Answer:
9 cm
Explanation:
The hypotenuse is the major side of the right triangle, if you look at the options only two of them are smaller than the hypotenuse, the rest cannot be the answer.
Hypotenuse (c) = 15 cm
Cathetus (a) = 12 cm
Cathetus (b) = ?
Equation:
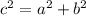
Solution:
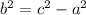
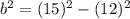
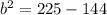
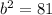
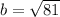
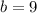
Hope this helps