let the normal force due to vertical wall is N1 and due to horizontal floor is N2
now by force balance we can say
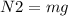
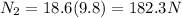
now friction force on the floor is given as
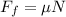
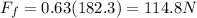
now by torque balance we will have
torque due to normal of vertical wall = torque due to weight of man
so here we have
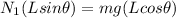
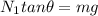
also we know that
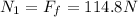
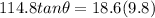
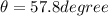
so above is the angle with the floor