Step-by-step explanation:
Isotopes are defined as the chemical species of the same element which differs in the number of neutrons. The isotopes which are unstable are known as radioactive isotope. A radioactive (unstable )isotope can undergo 3 decay process:
1. Alpha Decay: In this decay process, a larger nuclei decays into smaller nuclei by releasing alpha particle. The particle released has a charge of +2 and a mass of 4 units.
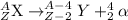
2. Beta-minus decay: In this decay process, a neutron gets converted into a proton and an electron. the particle released during this process is a beta-particle.
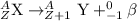
3. Beta-plus decay: In this decay process, a protons gets converted into a neutron and electron-neutrino particle. The particle released during this process is a positron particle.
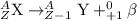
Isotopes which are unstable in nature can undergo these 3 decay processes.