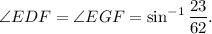Answer: The answers are (a) 40 cm and (b)
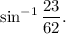
Step-by-step explanation: The calculations are as follows:
(a) See the figure (a). As given in the question, A circle with centre 'O' circumscribes a triangle ABC with BC = 20 cm and ∠BAC = 30°. We need to find the diameter DC of the circle.
Let us draw BD. Now, ∠BAC and ∠BDC are angles on the same arc BC, so we have
∠BAC = ∠BDC = 30°.
Also, ∠CBD = 90°, since it stands on the diameter DC. So, ΔBCD will be a right angled triangle.
We can write
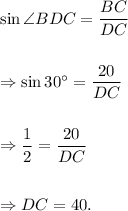
Thus, the diameter of the circle = 40 cm.
(b) See the figure (b).
As given in the question, A circle with centre 'O'' circumscribes a triangle DEF with EF = 4.6 inches and diameter GF = 12.4 in.. We need to find the angle EDF.
Let us draw GE. Now, ∠EGF and ∠EDF are angles on the same arc EF, so we have
∠EGF = ∠EDF = ?
Also, ∠GEF = 90°, since it stands on the diameter GF. So, ΔGEF will be a right angled triangle.
We can write
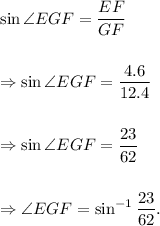
Thus,