For this case, we have the expression:
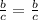
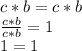
It is an example of identity.
Equality is met, the term that is on the left side of equality is identical to the term on the right side.
Identity property of the sum:
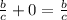
Identity property of multiplication:
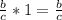
ANswer:
Identity
Option B