As we know that with respect to oxygen atom taken as reference the product of atomic mass and specific heat of a metal will remain constant.
this product is equal to 0.38
so here we will say that let atomic mass of the metal is M
so with respect to oxygen atom its mass is given as
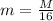
now we will have
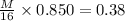
now we will have
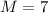
so atomic mass of the metal is 7 g/mol