Answer:
Right option is B. x = -3 ± 2√5
Explanation:
Given equation,
x² + 6x - 11 = 0
Using quadratic formula,
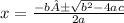
Comparing from general quadratic equation: ax² + bx + c = 0
Here, a= 1 b = 6 and c = -11
so,
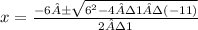
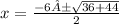
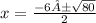
x = -3 ± 2√5
Hence right option is B. x = -3 ± 2√5