Answer:
The derivative of the function does not exist.
Explanation:
The alternative form of a derivative is given by:
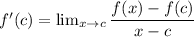
Our function is defined as:
h(x)=|x+8|
i.e. h(x)= -(x+8) when x+8<0
and x+8 when x+8≥0
i.e. h(x)= -x-8 when x<-8
and x+8 when x≥-8
Hence now we find the derivative of the function at c=-8
i.e. we need to find the Left hand derivative (L.H.D.) and Right hand derivative (R.H.D) of the function.
The L.H.D at a point 'a' is calculated as:
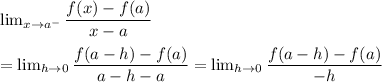
Similarly R.H.D is given by:
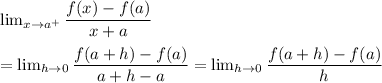
Now for L.H.D we have to use the function h(x) =-x-8
and for R.H.D. we have to use the function h(x)=x+8
L.H.D.
we have a=-8
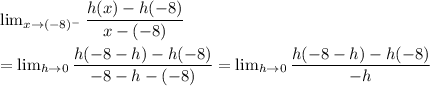
=
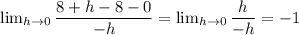
similarly for R.H.D.
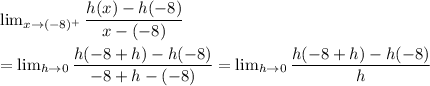
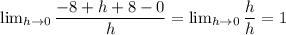
Now as L.H.D≠R.H.D.
Hence, the function is not differentiable.