Answer:
0.5 m/s
Explanation:
A 500 g model train car traveling at 0.8 m/s collides with a 300 g stationary car.
Initial velocity of train,
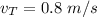
Initial velocity of car,
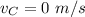
Mass of train,
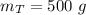
Mass of car,
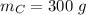
The cars hook up and move off down the track together.
Let the final velocity of car and train,
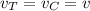
Using conservation of momentum,
Momentum before collision = Momentum after collision
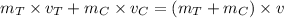
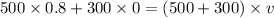
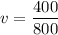
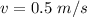
Hence, After collision they will going with 0.5 m/s