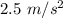If the speed of the car changes uniformly, as shown in the graph, this means that the acceleration is constant. As the acceleration is the derivative of the speed
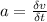
Then, this means that the acceleration is the slope of the equation of the line shown in the graph.
Then, we find the acceleration using the following equation:
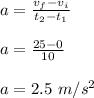
Then, the acceleration of the car is