For
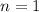 , on the left we have
, on the left we have
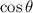 , and on the right,
, and on the right,
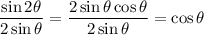
(where we use the double angle identity:
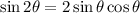 )
)
Suppose the relation holds for
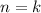 :
:
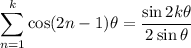
Then for
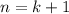 , the left side is
, the left side is
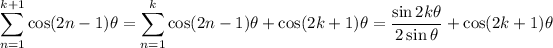
So we want to show that
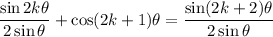
On the left side, we can combine the fractions:
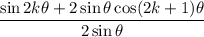
Recall that
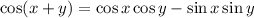
so that we can write
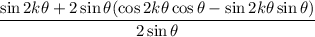
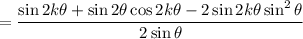
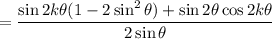
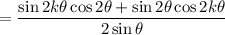
(another double angle identity:
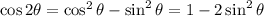 )
)
Then recall that
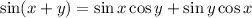
which lets us consolidate the numerator to get what we wanted:
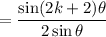
and the identity is established.