Answer:
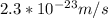
Step-by-step explanation:
Momentum (p) is defined as the product of the mass (m) and velocity (v) of an object:
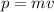
There are different types of momentum. Linear momentum (caused by the linear motion of te rock) and angular momentum (caused by the angular velocity of the earth).
Initial momentum of the falling rock equals zero, because its initial velocity is zero. To find the momentum change, we need its final value, for which we need its final velocity.
The kinematic formula, which relates final velocity (v), initial velocity (v0), acceleration (a) and falling distance (h) is:
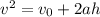
In this case:
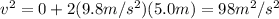
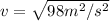
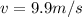
Now, the change in momentum (dp) of the rock is simply is simply:
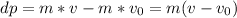
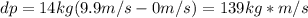
For closed systems (like this earth-rock system), momentum is conserved. It means that a change in rock's momentum equals to an opposite but in the same magnitude momentum change of the earth. The initial momentum of the earth is also equal to zero. Matching changes in momentum:
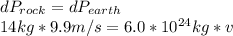
Solving for v:
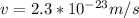
The, the change in earth's speed magnitude is 2.3*10^-23m/s