Answer:
For 1: The correct option is Option C.
For 3: The final velocity of the opponent is 1m/s
Explanation:
During collision, the energy and momentum remains conserved. The equation for the conservation of momentum follows:
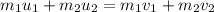 ...(1)
...(1)
where,
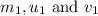 are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of first object
are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of first object
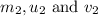 are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of second object
are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of second object
For 1:
We are Given:
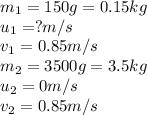
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
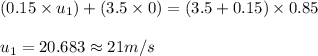
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Impulse is defined as the product of force applied on an object and time taken by the object.
Mathematically,
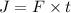
where,
F = force applied on the object
t = time taken
J = impulse on that object
Impulse depends only on the force and time taken by the object and not dependent on the surface which is stopping the object.
Hence, the impulse remains the same.
Let the speed in right direction be positive and left direction be negative.
We are Given:
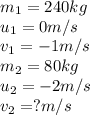
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
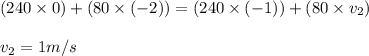
Hence, the final velocity of the opponent is 1m/s and has moved backwards to its direction of the initial velocity.