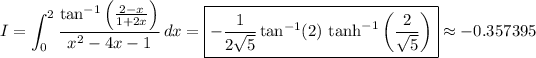There's nothing particularly tricky about the limits of integration. The upper limit is a telescoping series converging to 2,
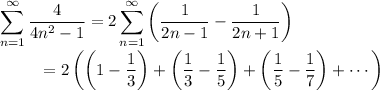
The lower limit reduces to 0 using the Riemann-Liouville definition of the fractional derivative. For
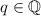 , let
, let
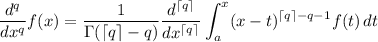
With
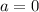 ,
,
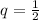 and
and
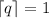 , it follows that
, it follows that
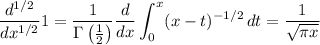
Let
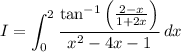
Observe that
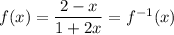
is its own inverse, so by substituting
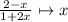 , we get the equivalent integral
, we get the equivalent integral
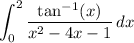
We have the identity
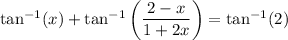
so that
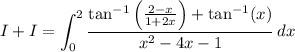
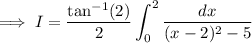
The remaining integral is trivial,
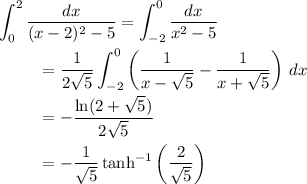
Then the integral we want is