Hi there!
Let's break this problem up into two parts.
Part A: Solenoid
The magnetic field everywhere inside a solenoid is constant, and can be found using the equation:
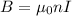
B = Magnetic field strength (? T)
μ₀ = Permeability of Free Space (4π × 10⁻⁷ Tm/A)
n = number of turns/meter (900)
I = current (0.03 A)
We are given all of these values, so let's solve.
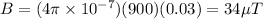
However, we also have a long wire that produces a magnetic field perpendicular to that produced by the solenoid.
Part B: Long wire
The equation for the magnetic field produced by a long wire is found by:
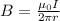
Where 'r' is the distance from the wire.
Plug in what we know:
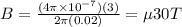
Now, we must do the vector sum of these two fields to find the total magnetic field. Since they are perpendicular (solenoid field points to the side, wire fire points in or out), we can use the Pythagorean Theorem.
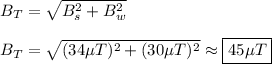
And here's our answer!