Answer:
The correct answer would be 48 percent.
It can be solved by using the Hardy-Weinberg equation.
p² + 2pq+ q² = 1
p + q = 1
where, p² represents homozygous dominant's frequency that is, SS in this case,
q² represents homozygous recessive's frequency that is, ss in this case,
2pq represents heterozygous dominant's frequency that is, Ss in this case.
p represents dominant allele's frequency and q represents the recessive allele's frequency.
Now, the percentage of homozygous recessive or short stems is 35%. Therefore, the frequency of homozygous recessive would be 0.35.
Thus, the value of q² = 0.35
So, q =
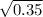 = 0.59 which is approximately equals to 0.6.
= 0.59 which is approximately equals to 0.6.
As p + q = 1 so, q = 1 - 0.6 = 0.4
The frequency of heterozygous (Ss) = 2pq = 2(0.6)(0.4) = 0.48
Hence, the frequency of heterozygous would be 48 percent.