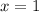Answer:
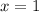
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
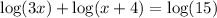
As the logs have no base, assume that the base is 10.
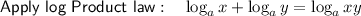
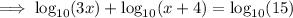
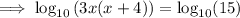
Expand the brackets:
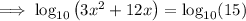
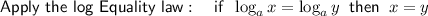
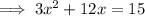
Subtract 15 from both sides:
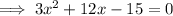
Factor out the common term 3:
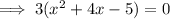
Divide both sides by 3:
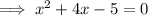
Split the middle term:
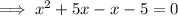
Factorize the first two terms and the last two terms separately:
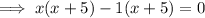
Factor out the common term (x + 5):
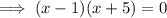
Therefore:
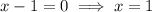
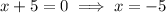
As logs cannot be taken of negative numbers,
 is an extraneous solution. Therefore, the only valid solution is:
is an extraneous solution. Therefore, the only valid solution is: