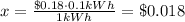1) 0.1 kWh
Step-by-step explanation:
The power of the lightbulb is:
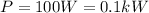
The energy used by the lightbulb is equal to the product between the power (P) and the time (t):
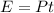
Since the bulb has been left on for t = 1 h, the total electrical energy used is
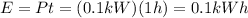
2) $ 0.018
Step-by-step explanation:
The company charges $0.18 per each kilowatt-hour. So, we can find the total cost charged for using 0.1 kWh of electricity by setting the following proportion:
$0.18 : 1 kWh = x : 0.1 kWh
And solving for x, we find