Answer: The calculations are done below.
Step-by-step explanation:
(i) Let the vertices be A(2,0), B(3,2) and C(5,1). Then,
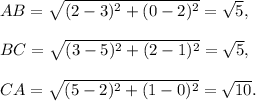
Since, AB = BC and AB² + BC² = CA², so triangle ABC here will be an isosceles right-angled triangle.
(ii) Let the vertices be A(4,2), B(6,2) and C(5,3.73). Then,
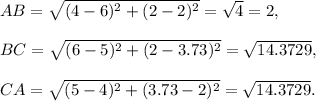
Since, BC = CA, so the triangle ABC will be an isosceles triangle.
(iii) Let the vertices be A(-5,2), B(-4,4) and C(-2,2). Then,
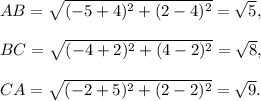
Since, AB ≠ BC ≠ CA, so this will be an acute scalene triangle, because all the angles are acute.
(iv) Let the vertices be A(-3,1), B(-3,4) and C(-1,1). Then,
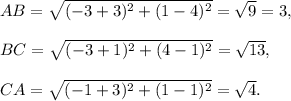
Since AB² + CA² = BC², so this will be a right angled triangle.
(v) Let the vertices be A(-4,2), B(-2,4) and C(-1,4). Then,
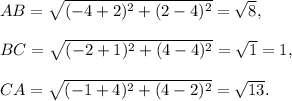
Since AB ≠ BC ≠ CA, and so this will be an obtuse scalene triangle, because one angle that is opposite to CA will be obtuse.
Thus, the match is done.