Answer:- 0.0211 moles of air.
Solution:- This problem is based on an ideal gas law equation.
temperature, pressure and volume are given and asked to calculate the moles of the air. Standard pressure is 1.00 atm.
T = 15 + 273 = 288 K
P = 1.00 atm
V = 0.500 L
The ideal gas law equation is, PV = nRT
where R is the universal gas law constant and its value is 0.0821 atm.L per mol per K.
n is the number of moles and its what we are asked to calculate.
For n, the equation is rearranged as:
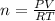
Let's plug in the values and do the calculations:
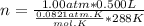
n = 0.0211 moles
So, there are 0.0211 moles of the air in the bottle.