At step 2, we arrive at
(2x + 3) (x + 3) = 0
and the next step (which isn't actually shown) is to use the so-called zero-product property that says if
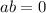 , then
, then
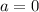 or
or
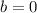 . This means
. This means
2x + 3 = 0 or x + 3 = 0
and solving the first equation leads to the rational solution.
2x + 3 = 0
2x = -3
x = -3/2