Answer:
C. 4
Explanation:
After plotting the curves, we get the figure given below.
So, the rectangle will lie in 1st and 2nd quadrant.
Thus, let the vertex in the 1st quadrant = ( x,y ) and in 2nd quadrant = ( -x,y ).
Then, the length of the rectangle = 2x and width of the rectangle = y.
As, area of a rectangle = length × width
Therefore, area of the given rectangle, A = 2x × y
i.e.
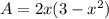
i.e.
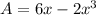
Thus, differentiating with respect to x and equating to 0 gives,
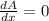
i.e.
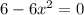
i.e.
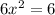
i.e.
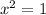
i.e.
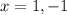
Again, differentiating with respect to x gives us
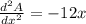 .
.
If x = -1 ,
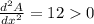 .
.
If x =1 ,
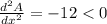 . This gives us that the maximum value of the area is obtained at x = 1.
. This gives us that the maximum value of the area is obtained at x = 1.
Thus, length = 2x = 2 and width = y =
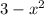 = 3- 1 = 2
= 3- 1 = 2
So, area of the rectangle is A = 2(1) × 2 = 4.
Hence, area of the rectangle is 4
 .
.