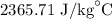Answer:
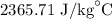
Step-by-step explanation:
V = Voltage = 230 V
I = Current = 1.8 A
 = Temperature change =
= Temperature change =
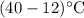
t = Time taken = 2 minutes
m = Mass of liquid = 750 g
c = Specific heat capacity of the liquid
Energy required to heat the water is equal to the heat released due to current passing
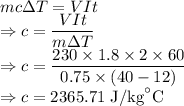
The specific heat capacity of the liquid is