Answer:
Ve = 0.01625 [m³]
Step-by-step explanation:
This type of problem can be solved by the following expression.
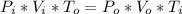
where_
Pi = Initial pressure = 2.5 x 10⁵ [Pa]
Vi = initial volume = 1.5 x 10⁻² [m³]
To = final temperature = 302 [K]
Po = final pressure = 1.2 x 10⁵ [Pa]
Vo = final volume [m³]
Ti = initial temperature = 302 [K]
Now the key to solving this problem is to make it clear that the temperature remains constant throughout the process. That is, it does not change.
![2.5*10^(5)*1.5*10^(-2) *302 = 1.2*10^(5)*V_(o)*302\\1132500=36240000*V_(o)\\V_(o)=0.03125 [m^(3) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/gp0fkwjhz21xjfjkkw8zqj4juerdmpht3j.png)
But this calculated volume corresponds to the volume of the tank, now by means of the difference between the initial volume and the final volume we can calculate the volume of gas that escaped.
![V_(e)=0.03125-0.015\\V_(e)=0.01625 [m^(3) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/ihi8gpymty697u9ste0oju49r0pcnpc4qn.png)