Answer:
Infinite Solutions
Explanation:
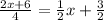
Get rid of the denominators by multiplying all whole equation by 4.
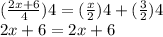
The interesting part is here. Both sides are same, meaning that if we continue to solve for the equation.
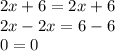
The equation is indeed true. Meaning that both graphs are the same and intercept both each others infinitely.
Therefore the answer is Infinite solution.