Answer:
P = 66.67 W
Step-by-step explanation:
Joule Heating
It's the process by which the electric current passing through a conductor produces heat.
Also known as Joule's first law or the Joule–Lenz law, states that the power of heating generated by an electrical conductor (P) is proportional to the product of its resistance (R) and the square of the current (I).
It can be described by the equation that follows:
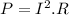
Also, we can calculate the voltage V with the formula of Ohm's law:
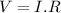
Combining both equations, power can be related to the voltage:
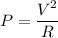
Given the power and the voltage, the resistance can be calculated by solving for R:
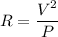
There are two bulbs marked P=200W V=250V and P=100 W V=250.
The first bulb has a resistance of:
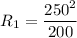
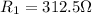
The first bulb has a resistance of:
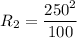
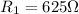
When connected in series, the total resistance is
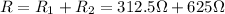
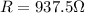
The total power consumed when connecting them to a V=250 V supply is:
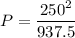
P = 66.67 W