The fully factorized third term of the arithmetic sequence is
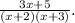
The arithmetic sequence is defined by the terms
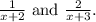
To find the common difference, subtract the first term from the second:
![\[d = (2)/(x + 3) - (1)/(x + 2).\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/zsvkszd6cc9d82zw9icirs2cx5we075i0q.png)
To combine the fractions, find a common denominator:
![\[d = (2(x + 2) - (x + 3))/((x + 2)(x + 3)).\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ok4dwnn3df4969gjsv24i18fuls5bmzvwb.png)
Simplify the numerator:
![\[d = (2x + 4 - x - 3)/((x + 2)(x + 3)) = (x + 1)/((x + 2)(x + 3)).\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/seohtutqj1hq9qib2wewoq4zbc7l9cgf0m.png)
Now, the third term can be found by adding the common difference to the second term:
![\[T_3 = (2)/(x + 3) + (x + 1)/((x + 2)(x + 3)).\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ql90oj43i94em5c9s3vmm8gt31g84cx9lm.png)
To add the fractions, find a common denominator:
![\[T_3 = (2(x + 2) + (x + 1))/((x + 2)(x + 3)).\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/409cy8vmwvxds17492n0isckfh0ae8cnkc.png)
Simplify the numerator:
![\[T_3 = (3x + 5)/((x + 2)(x + 3)).\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/44yh7xwd3yaro82enfcld2f79dg6ifkc7z.png)
Therefore, the fully factorized third term of the arithmetic sequence is
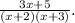
The probable question may be:
The first two terms of an arithmetic sequence are shown below. 1 /x+2, 2/x+3' . Find the third term of this sequence. Give your answer fully factorised.