Answer:
Explanation:
Given that:
The sample mean
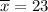
The standard deviation
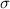 = 9
= 9
Population mean = 20
Null hypothesis:
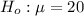
Alternative hypothesis:
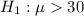
(a)
When Sample size = 10
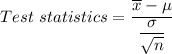
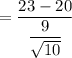
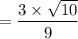
t = 1.0541
Degree of freedom df:
df = n -1
df = 10 - 1
df = 9
P(value) for t = 1.0541 at df = 9:
P(value) = P(Z > 1.0541)
P(value) = 1 - P(< 1.0541)
P(value) = 1 - 0.8403
P(value) = 0.1597
There is no enough evidence to infer at the 5% significance since p-value is greater than the level of significance.
(b) When sample size = 30
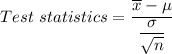
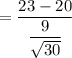
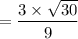
t = 1.8257
Degree of freedom df:
df = n -1
df = 30 - 1
df = 29
P(value) for t = 1.8257 at df = 29:
P(value) = P(Z > 0.9609)
P(value) = 1 - P(< 0.9609)
P(value) = 1 - 0.9609
P(value) = 0.0391
There is enough evidence to infer that the mean is greater than 20 at the 5% significance level as the p-value is less than the significance level.
(c) When sample size = 50
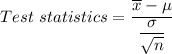
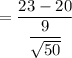
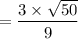
t = 2.3570
Degree of freedom df:
df = n -1
df = 50 - 1
df = 49
P(value) for t = 2.3570 at df = 49:
P(value) = P(Z > 0.9888)
P(value) = 1 - P(< 0.9888)
P(value) = 1 - 0.9888
P(value) = 0.0112
There is enough evidence to infer that the mean is greater than 20 at the 5% significance level as the p-value is less than the significance level.