The total volume of gas present at the end of the reaction : 100 cm³
Further explanation
Given
100cm³ of hydrogen is mixed with 25cm³ of oxygen
Reaction
2H₂(g) + O₂(g) ===> 2H₂O(l)
Required
The total volume of gas
Solution
From Avogadro's hypothesis, at the same temperature and pressure, the ratio of gas volume will be equal to the ratio of gas moles
Find limiting reactant
mol ratio H₂(g) : O₂(g) from equation : 2 : 1, so volume ratio = 2 : 1
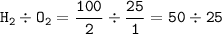
O₂ as a limiting reactant(smaller ratio), so the remaining H₂(as excess reactant) = 100 cm³ - 50 cm³(reacting hydrogen) =50 cm³
H₂O formed from O₂ = 2 x volume O₂ = 2 x 25 = 50 cm³
2H₂(g) + O₂(g) ===> 2H₂O(l)
100 25 0
50 25 50
50 0 50
Total volume gas present : volume H₂ + volume H₂O = 50 + 50 = 100 cm³