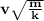Answer:
The distance that the spring compresses is:
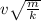
Step-by-step explanation:
Kinetic and Elastic Potential Energy
The kinetic energy of an object of mass m traveling at a speed v is:
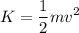
The elastic potential energy of a spring of constant k that compresses a distance x is:
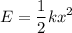
The block of mass m is moving at a speed v when compresses a spring of constant k. The kinetic energy will eventually transform into elastic energy, but before that, both energies will be equal. It happens when:
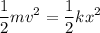
Simplifying:
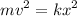
Dividing by k:
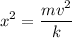
Taking square root:
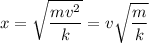
The distance that the spring compresses is