Answer:
Part I)

Giving the equation:

Part II)
(-1, 2)
Explanation:
We have the equation:

Where a and c are constants.
We are given gradient/slope of the curve at the point (1, 2) is -2.
Part I)
We know that the gradient of the curve exactly at the point (1, 2) is -2.
So, we will differentiate our equation. We have:

Differentiate both sides with respect to x:
![\displaystyle y^\prime=(d)/(dx)\big[ax^3+x+c\big]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/cni669nc9mdzr2mfgsqg12ss1rzxidns40.png)
Expand the right:
![\displaystyle y^\prime=(d)/(dx)\big[ax^3]+(d)/(dx)\big[x\big]+(d)/(dx)\big[c\big]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/b2jsuv9wakrp9iswqxp74vqyy9r5spy8av.png)
Since a and c are simply constants, we can move them outside:
![\displaystyle y^\prime=a(d)/(dx)\big[x^3]+(d)/(dx)\big[x\big]+c(d)/(dx)\big[1\big]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/fbo4e4tp5xco7gotpk8abmer7tagejqfqj.png)
Differentiate. Note that the derivative of a constant is simply 0.

We know that at the point (1, 2), the gradient/slope is -2.
Hence, when x is 1 and when y is 2, y’ is -2.
So (we don’t have a y so we can ignore it):

Solve for a. Simplify:

Subtract 1 from both sides yield:
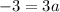
So, it follows that:

Therefore, our derivative will be:
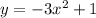
Now, we can go back to our original equation:

Since we know that a is -1:

Recall that we know that a point on our curve is (1, 2).
So, when x is 1, y is 2. By substitution:

Solve for c. Simplify:

Then it follows that:
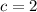
Hence, our entire equation is:

Part II)
Our derivative is:

If the gradient is -2, y’ is -2. Hence:

Solve for x. Subtracting 1 from both sides yields:

So:
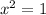
Then it follows that:

Since we already have the point (1, 2) where x is 1, our other point is where x is -1.
Using our equation:

We can see that our second point is:

Simplify:

So, our second point where the gradient is -2 is at (-1, 2).