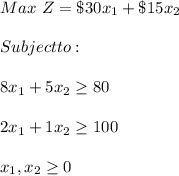Answer:
Follows are the solution to this question:
Explanation:
In this question, some of the data is missing, that's why this question can be defined as follows:
It Includes an objective feature coefficient, its sensitivity ratio is the ratio for values on which the current ideal approach will remain optimal.
When there is Just one perfect solution(optimal solution) then the equation is:
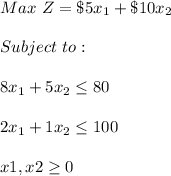
When there are Several perfect solutions then the equation is:
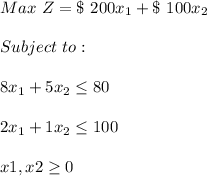
When there is also no solution, since it is unlikely then the equation is:
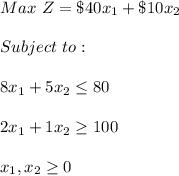
When there is no best solution since it is unbounded then the equation is: