Answer:
The longest wavelength of light needed to produce current is 567.9 nm.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
minimum energy required to produce electric current from the cathode to anode = work function, E = 3.5 x 10⁻¹⁹ J
E = hf
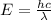
where;
c is speed of light = 3 x 10⁸ m/s
λ is the longest wavelength of light needed to produce current
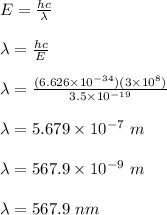
Therefore, the longest wavelength of light needed to produce current is 567.9 nm.