Answer: 1.95 g of oxygen is present.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Dalton's law, the total pressure is the sum of individual pressures.
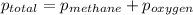
Given :
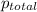 =total pressure of gases = 727 mm Hg
=total pressure of gases = 727 mm Hg
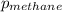 = partial pressure of methane = 571 mm Hg
= partial pressure of methane = 571 mm Hg
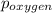 = partial pressure of oxygen = ?
= partial pressure of oxygen = ?
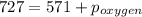
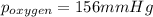
Also
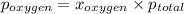
Given : 3.62 g of methane is present
moles of methane =
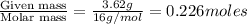
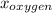 = mole fraction of oxygen
= mole fraction of oxygen
=
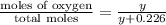
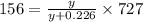
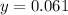
mass of oxygen =
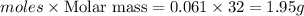
Thus 1.95 g of oxygen is present.