Answer:
a. t = 2.02 s
b. d = 20.2 m
Step-by-step explanation:
Horizontal Motion
If an object is thrown horizontally from a height h with a speed v, it describes a curved path ruled exclusively by gravity until it eventually hits the ground.
The time the object takes to hit the ground can be calculated as follows:
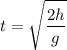
The time does not depend on the initial speed.
The range or maximum horizontal distance traveled by the object can be calculated by the equation:
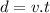
The man standing on the edge of the h=20 m cliff throws a rock with an initial horizontal speed of v=10 m/s.
a.
The time taken by the rock to reach the ground is:
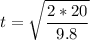
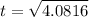
t = 2.02 s
b.
The range is:
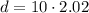
d = 20.2 m