Answer:
a)
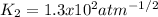
b)
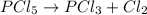
![[PCl_5]=0.0375M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ogjd215d3dodqzph1jfum5kr5jx9ckbw7r.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
a) In this case, since we can see that the second reaction is equal to the half of the first reaction, we can relate the equilibrium constants as shown below:
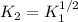
Thus, by plugging in the the equilibrium constant of the first reaction we obtain:
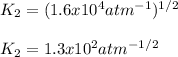
b) In this case, for the described reaction we can write:
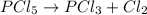
Thus, the corresponding equilibrium expression is:
![K=([PCl_3][Cl_2])/([PCl_5])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8rcik22jasz8hoqc5atedq0qs0zt3lswea.png)
In such a way, since we know the equilibrium constant and the concentrations of PCl3 and Cl2 at equilibrium, we can compute the concentration of PCl5 at equilibrium as follows:
![[PCl_5]=([PCl_3][Cl_2])/(K)\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/i5f29vblpth2609v91tdjptknotalmop4t.png)
![[PCl_5]=((0.20mol)/(4L) *(0.12mol)/(4L) )/(0.04)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lhq4s382cvcrmqa3jc7h6w93k15l0twn4k.png)
![[PCl_5]=0.0375M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ogjd215d3dodqzph1jfum5kr5jx9ckbw7r.png)
Best regards!