Answer:
29273.178 joules have been added to the gas for the entire process.
Step-by-step explanation:
The specific heats of monoatomic gases, measured in joules per mol-Kelvin, are represented by the following expressions:
Isochoric (Constant volume)
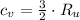 (1)
(1)
Isobaric (Constant pressure)
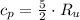 (2)
(2)
Where
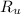 is the ideal gas constant, measured in pascal-cubic meters per mol-Kelvin.
is the ideal gas constant, measured in pascal-cubic meters per mol-Kelvin.
Under the assumption of ideal gas, we notice the following relationships:
1) Temperature is directly proportional to pressure.
2) Temperature is directly proportional to volume.
Now we proceed to find all required temperatures below:
(i) Alice heats the gas at constant volume until its pressure is doubled:
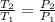 (3)
(3)
(
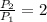 ,
,
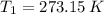 )
)
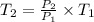
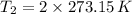
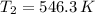
(ii) Bob further heats the gas at constant pressure until its volume is doubled:
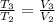 (4)
(4)
(
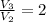 ,
,
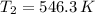 )
)
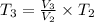
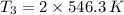
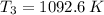
Finally, the heat added to the gas (
 ), measured in joules, for the entire process is:
), measured in joules, for the entire process is:
![Q = n\cdot [c_(v)\cdot (T_(2)-T_(1))+c_(p)\cdot (T_(3)-T_(2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/sxl1l7s4xm3jy9pkxj78dk2e129nhzfj2h.png) (5)
(5)
If we know that
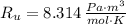 ,
,
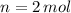 ,
,
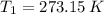 ,
,
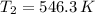 and
and
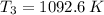 , the heat added to the gas for the entire process is:
, the heat added to the gas for the entire process is:
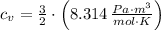
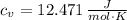
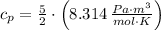
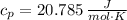
![Q = (2\,mol)\cdot \left[\left(12.471\,(J)/(mol\cdot K) \right)\cdot (536.3\,K-273.15\,K)+\left(20.785\,(J)/(mol\cdot K) \right)\cdot (1092.6\,K-546.3\,K )\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vvssfnbxvmhgu1jelh5ko1zxecdwmldead.png)
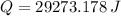
29273.178 joules have been added to the gas for the entire process.