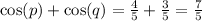We know that ,
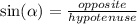
and
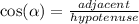
where 'alpha' is an angle of triangle ; 'opposite' denotes the side opposite to alpha & 'adjacent' refers to the side next to the angle (but not hypotenuse)
Similarly ,
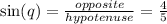
Let the length of the opposite side be 4x and the length of hypotenuse be 5x. By using Pythagorean Theorem , we can find the length of base.
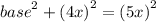
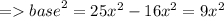
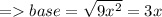
Now , we have got the length of all the sides of the triangle. So,
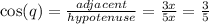
and
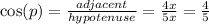
So,