Answer:
The work function of the metal is 2.226 eV.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
wavelength of the violet light, λ = 427 nm = 427 x 10⁻⁹ m
maximum kinetic energy, K.E = 0.684 eV
The energy of the incident light is calculated as;
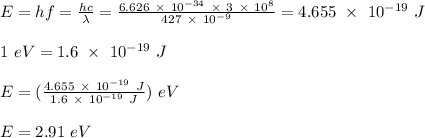
Apply Einstein's photoelectric equation;
E = Ф + K.E
where;
Ф is the work function of the metal
Ф = E - K.E
Ф = 2.91 eV - 0.684 eV
Ф = 2.226 eV.
Therefore, the work function of the metal is 2.226 eV.