Answer:
![Rate=k[A]^m[B]^n](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/17gf2f50x7lkwrk3h9a3xdbt3r3anzvsir.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
![Rate=k[A]^m[B]^n](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/17gf2f50x7lkwrk3h9a3xdbt3r3anzvsir.png)
k= rate constant
m = order with respect to A
n = order with respect to B
Total order = m+n
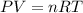 is ideal gas equation
is ideal gas equation
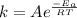 is vant hoff equation.
is vant hoff equation.
![K_(eq)=([C]^c[D]^d)/([A]^a[B]^b)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jbd7uq80565lgtnpqjte86knmd4rxyi07m.png) is equilibrium constant.
is equilibrium constant.