Answer: The concentration of Pb2+ in the anode compartment is
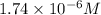
Step-by-step explanation:

Here Pb undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons, thus act as anode. Sn undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
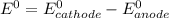
Where both
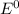 are standard reduction potentials.
are standard reduction potentials.
![E^0_([Sn^(2+)/Sn])=-0.14V](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/h9p8nh5hsyhxlf4oxkw126pyrl93cmn2mf.png)
![E^0_([Pb^(2+)/Pb])=-0.13V](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hu0kxwtirq0o0w6wjysl2j78dmqc2cldga.png)
![E^0=E^0_([Sn^(2+)/Sn])- E^0_([Pb^(2+)/Pb])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/2d54toajcvpoeemlqlv8sr3po9f0hhcjht.png)
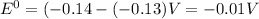
Now using Nernst Eqn :
![E=E^0-(0.059)/(n)\log([Pb^(2+)])/([Sn^(2+)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/evm5w6chzmusx5nywz23fjjdmbtl2fqdt7.png)
![0.16=(-0.01)-(0.059)/(2)\log([Pb^(2+)])/([1.00])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ca896r04o54xa7agmcd1k72t7s4zxj4jjq.png)
![0.17=-0.0295\log([Pb^(2+)])/([1.00])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/m37vmnmurfpn029lk96gg7swvs2idpd943.png)
![-5.76=\log([Pb^(2+)])/([1.00])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/kmetupvfke6ixyz19s4odt6s8trw0q6qlu.png)
![1.74* 10^(-6)=([Pb^(2+)])/([1.00])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/d400li1za21v98ruokk9xo4m7tynyvejm1.png)
![[Pb^(2+)]=1.74* 10^(-6)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lu8xnkr935kypc01oq0rukiidocg0poxap.png)