Answer:
Part A)
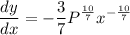
Part B)
The daily operating cost decreases by about $143 per extra worker.
Explanation:
We are given the equation:
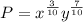
Where P is the number of eggs laid, x is the number of workers, and y is the daily operating budget (assuming in US dollars $).
A)
We want to find dy/dx.
So, let’s find our equation in terms of x. We can raise both sides to 10/7. Hence:
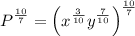
Simplify:
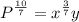
Divide both sides by the x term to acquire:
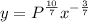
Take the derivative of both sides with respect to x:
![\displaystyle (dy)/(dx)=(d)/(dx)\Big[P^(10)/(7)x^{-(3)/(7)}\Big]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/77csndop2p1s4xf7g0pzxr0ati9gt2qt3p.png)
Apply power rule. Note that P is simply a constant. Hence:
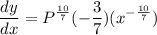
Simplify. Hence, our derivative is:
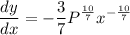
Part B)
We want to evaluate the derivative when x is 30 and when y is $10,000.
First, we will need to find P. Our original equations tells us that:
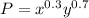
Hence, at x = 30 and at y = 10,000, P is:
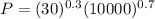
Therefore, for our derivative, we will have:
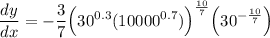
Use a calculator. So:
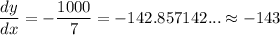
Our derivative is given by dy/dx. So, it represents the change in the daily operating cost over the change in the number of workers.
So, when there are 30 workers with a daily operating cost of $10,000 producing a total of about 1750 eggs, the daily operating cost decreases by about $143 per extra worker.