Answer:
See the explanation below
Step-by-step explanation:
Since the bus travels at a constant speed, we can use the following equation.
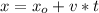
where:
x = final position [m]
xo = initial position = 0 (if the bus starts from some reference point)
v = constant velocity [m/s]
t = time [s]
Let's take some data as an example and then graph them.
v = 2 [m/s]
t = 2 [s]
That is, after two seconds, the final position will be:
![x = 0 + 2*2\\x = 4 [m]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/cg11nyl65cgmtw6c8oenp3m0cazgc18atp.png)
After the two seconds, the bus stops for about 2 seconds more. Then the bus will go with a velocity of 4 [m/s] for two seconds more.
So the total time is 6 [s].
Let's draw the x-t graph.
- We see that the position changes during the first two seconds, from a position 0 to 4 [m]
- Then the bus stops for two seconds, that is, for 4 seconds the bus has traveled 4 meters.
- Then the bus moves to 4 [m/s], for 2 more seconds. That is, the bus will have moved up to 6 seconds.
And the final offset must be calculated using the same equation.
![x = x_(0)+v*t\\x = 4+4*(6-4)\\x = 4 +8\\x = 12 [m]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/high-school/81mpm0simc3cyz4wdgkdrgkr7kgt16wvlr.png)