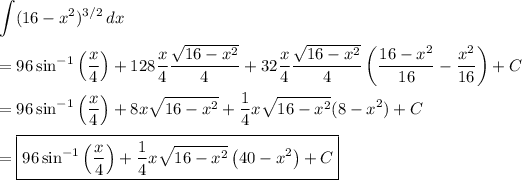Substitute
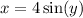 , so that
, so that
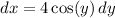 . Part of the integrand reduces to
. Part of the integrand reduces to
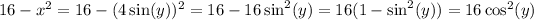
Note that we want this substitution to be reversible, so we tacitly assume
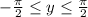 . Then
. Then
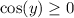 , and
, and
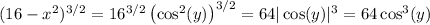
(since
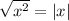 for all real
for all real
 )
)
So, the integral we want transforms to
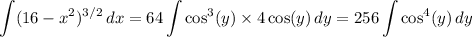
Expand the integrand using the identity
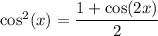
to write
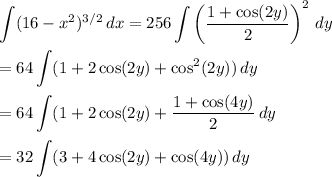
Now integrate to get
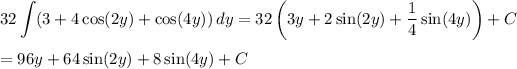
Recall the double angle identity,
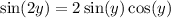
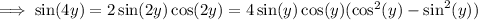
By the Pythagorean identity,
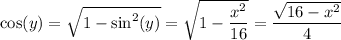
Finally, put the result back in terms of
 .
.