Answer:
(c) f^-1(x) = (x -1)/2
Explanation:
The inverse function will give x-values when f(x) values are supplied as arguments. The function can be determined either by using table values to write the function, or by checking the offered functions against the table values.
__
checking
We want to find f^-1(x) such that f^-1(-3) = -2, matching the first line of the table.
- A: (-3 +1)/-2 = 1 ≠ -2
- B: 1/2(-3) -1 = -5/2 ≠ -2
- C: (-3 -1)/2 = -2 . . . . . . . . . this function matches the table
- D: -2(-3) -1 = 5 ≠ -2
The equation representing f^-1(x) is ,..
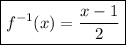
__
writing
We can use the first two points in the table to determine the required inverse function:
(x, f^-1(x)) = (-3, -2) and (-1, -1)
The slope is ...
m = (y2 -y1)/(x2 -x1) = (-1 -(-2))/(-1 -(-3)) = 1/2
The y-intercept is ...
b = y1 -m(x1) = -2 -(1/2)(-3) = -1/2
Then the equation of f^-1(x) is ...
y = mx +b
f^-1(x) = 1/2x -1/2 = (x -1)/2